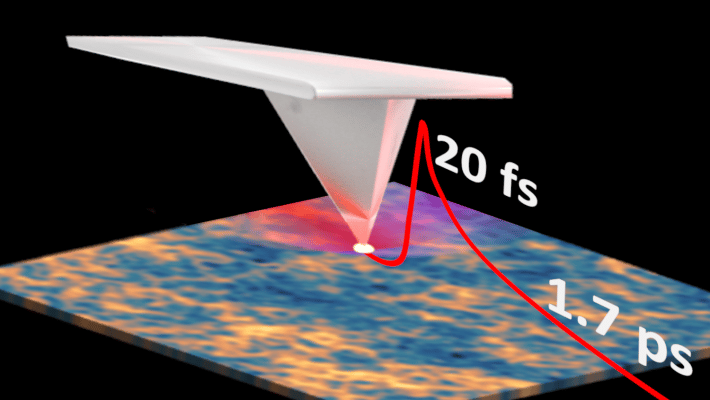
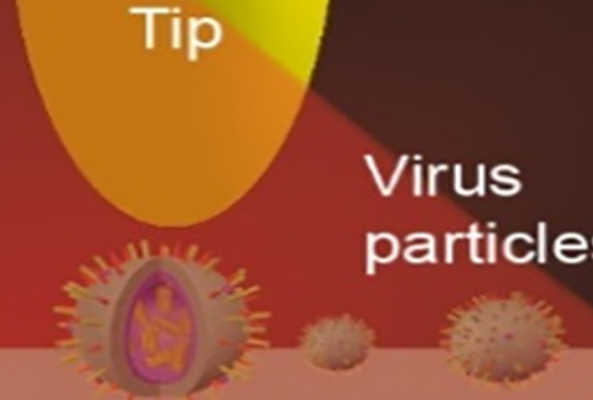
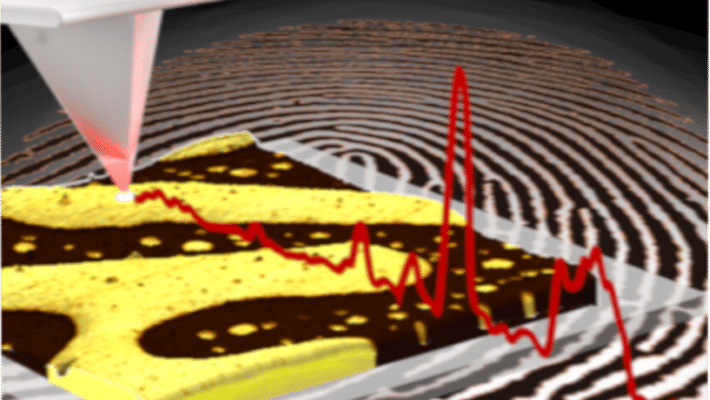
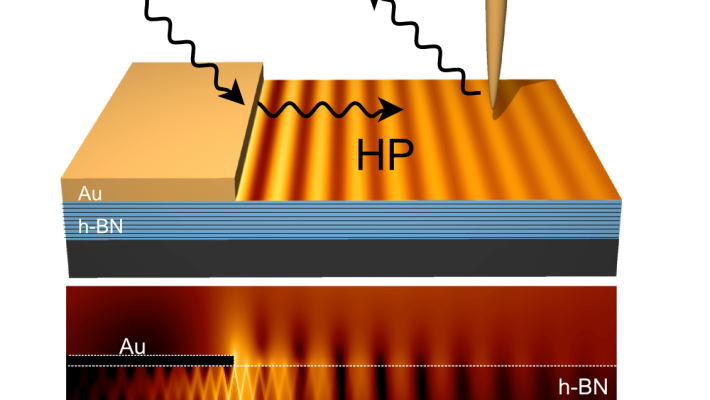
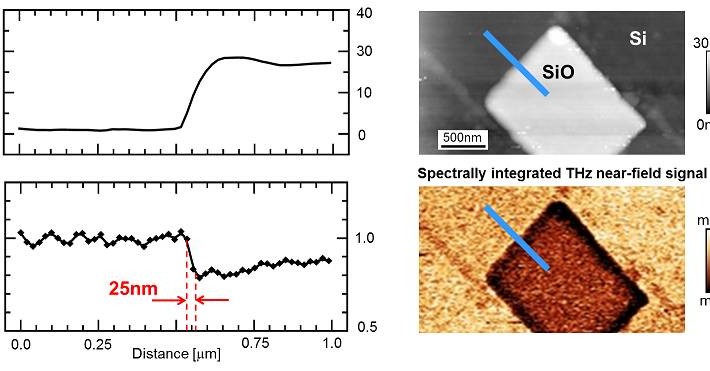
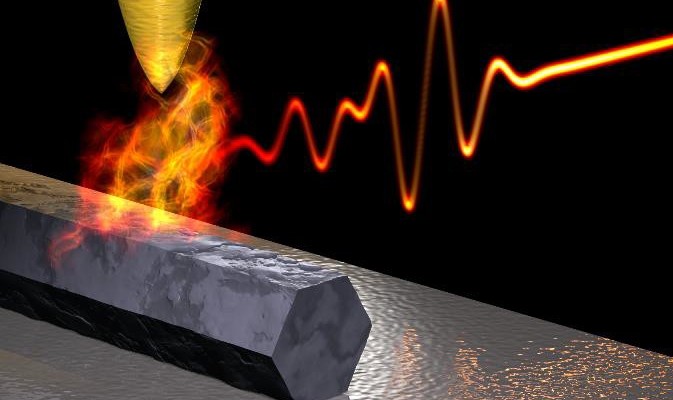
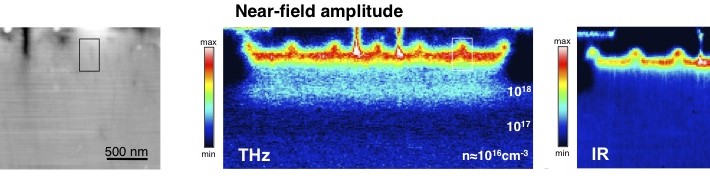
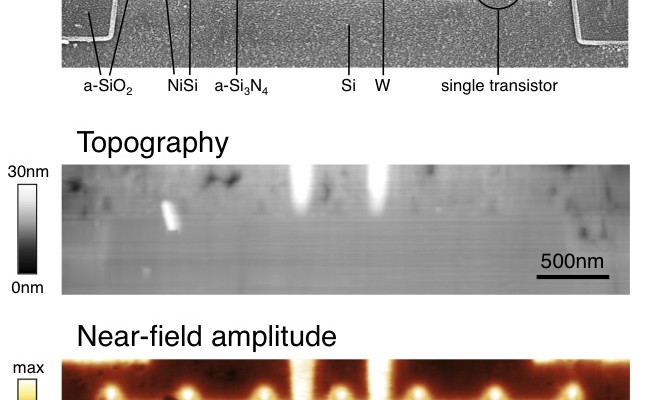
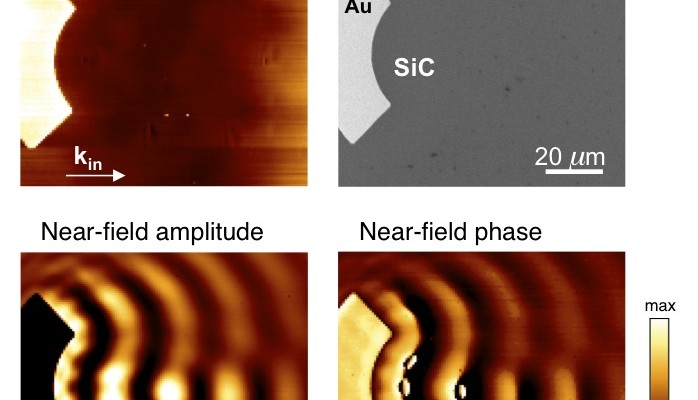
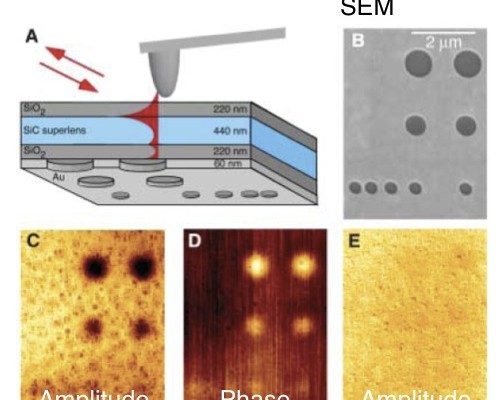
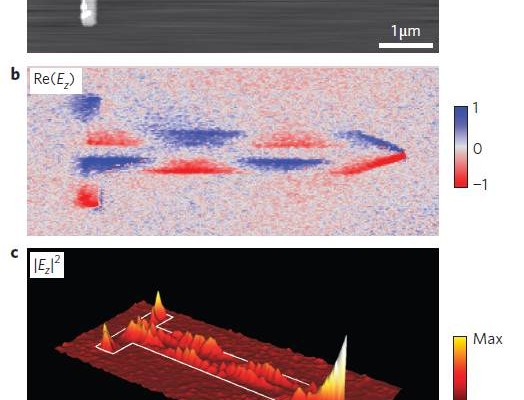
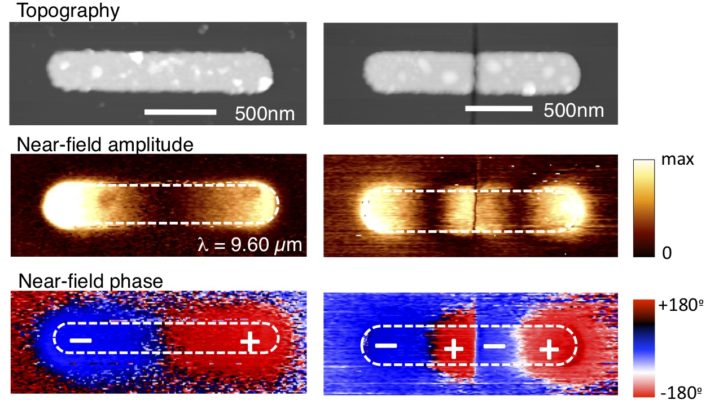
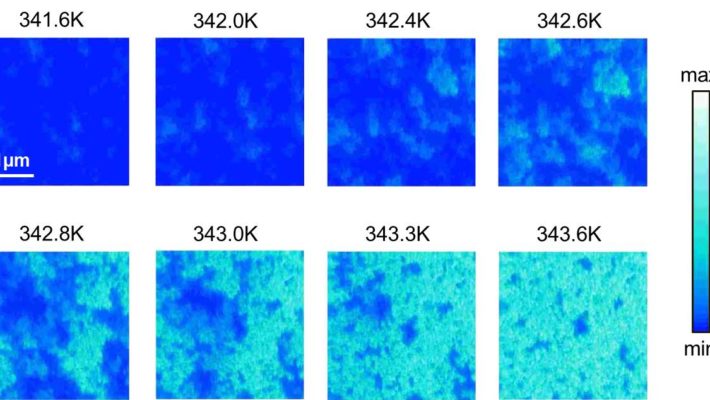
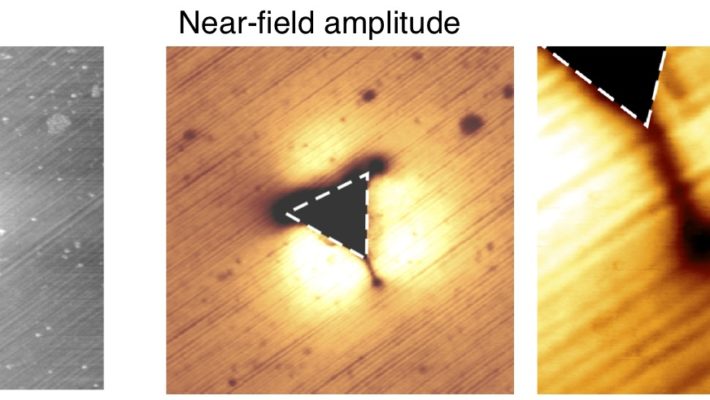
Ultrafast pump-probe nanoscopy enables study of dynamic processes in nano-materials by providing time-resolved spectroscopy with nanoscale spatial resolution. This e-book summarizes pioneering applications collection studies related to ultrafast science using ultrafast pup-probe nanoscopy. A novel breakthrough technology with amazing funding success-rates, influencing already diverse research areas. Download E-Book